API Gateway vs Load Balancer
(4 Minutes) | How They Work, Benefits, Pitfalls, Where and When to Use Each
Get our Architecture Patterns Playbook for FREE on newsletter signup:
Phoenix.new – The Remote AI Runtime for Phoenix
Presented by Fly.io
A cloud-native, AI‑powered development environment for Elixir/Phoenix. It lets you describe an app and an LLM-driven agent boots a real Phoenix project in the browser, complete with:
Full root-shell access in an isolated VM
A browser-based IDE and headless browser testing, live preview URLs, and GitHub integration
Built using Fly.io infrastructure. Code is fully exportable
Apps start from a standard phx .new template (using SQLite), so you can clone and run them locally
Interactive, live testing and Full-stack support
The agent creates a fully designed mockup and builds all the way to a working real-time app.
API Gateway vs Load Balancer
They both sit in front of your services.
They both route traffic.
They can both speak HTTP.
But an API Gateway and a Load Balancer solve very different problems.
Knowing the difference is crucial when you’re scaling systems or designing microservice architectures.
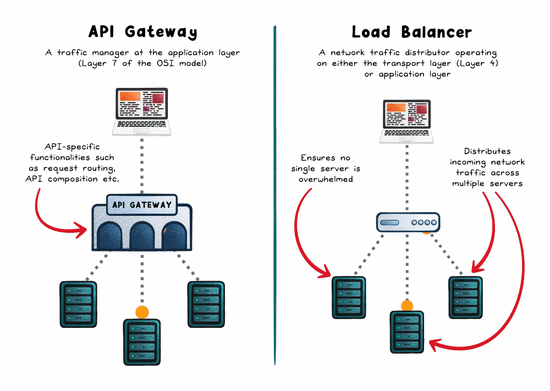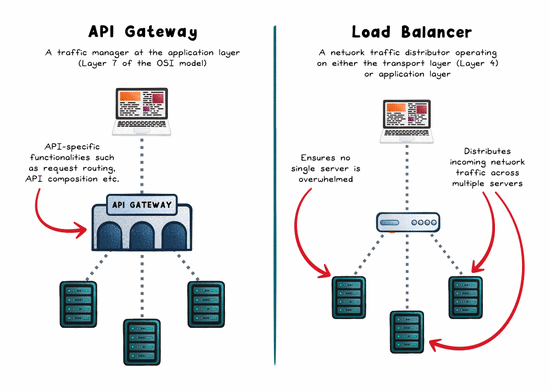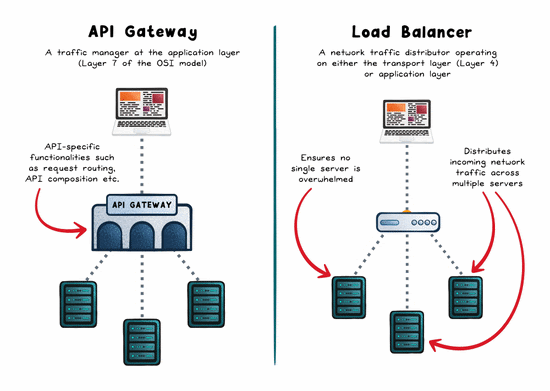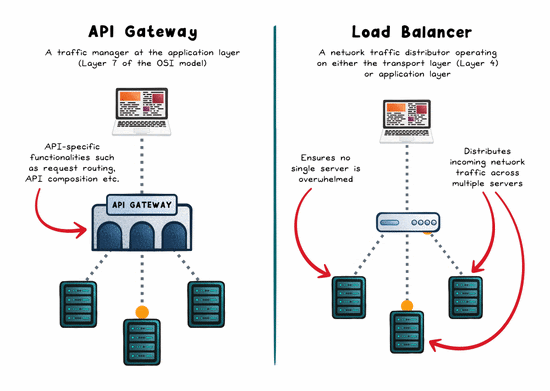
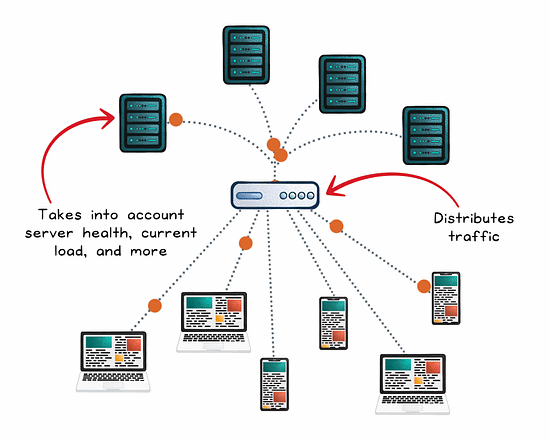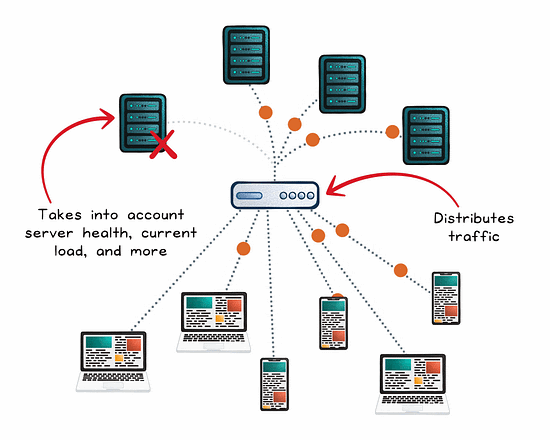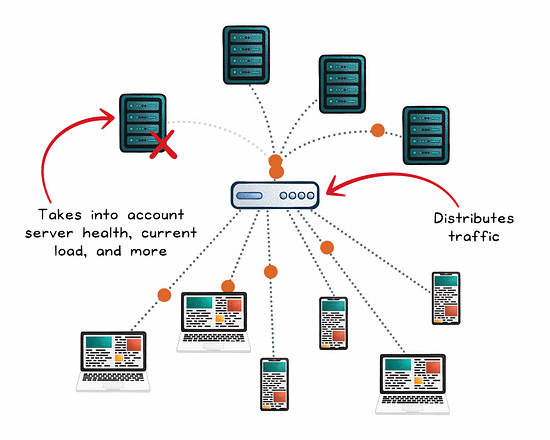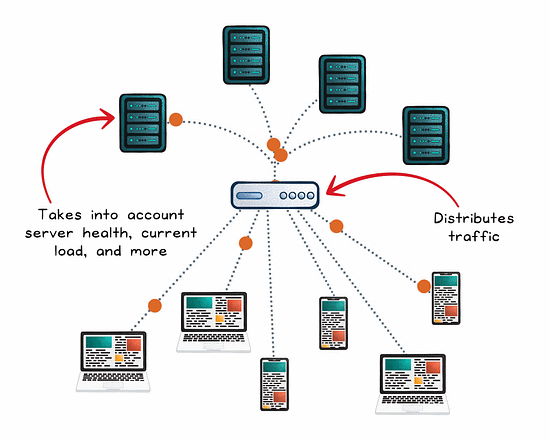
The Role of a Load Balancer
A load balancer is concerned with distributing traffic across multiple servers to prevent any one instance from becoming a bottleneck. The goal: maximize throughput, reduce response time, and maintain availability.
Load balancer in action:
Client requests are sent to the load balancer instead of directly to your servers.
The load balancer picks a healthy server using a routing algorithm (round robin, least connections, weighted, etc).
The request is forwarded to the chosen server.
The server processes the request and returns the result to the load balancer.
The load balancer sends the response back to the client.
Key strengths:
Health checks and failover
Cross-zone/region traffic distribution
TLS termination
Scaling horizontally without exposing individual servers
The Role of an API Gateway
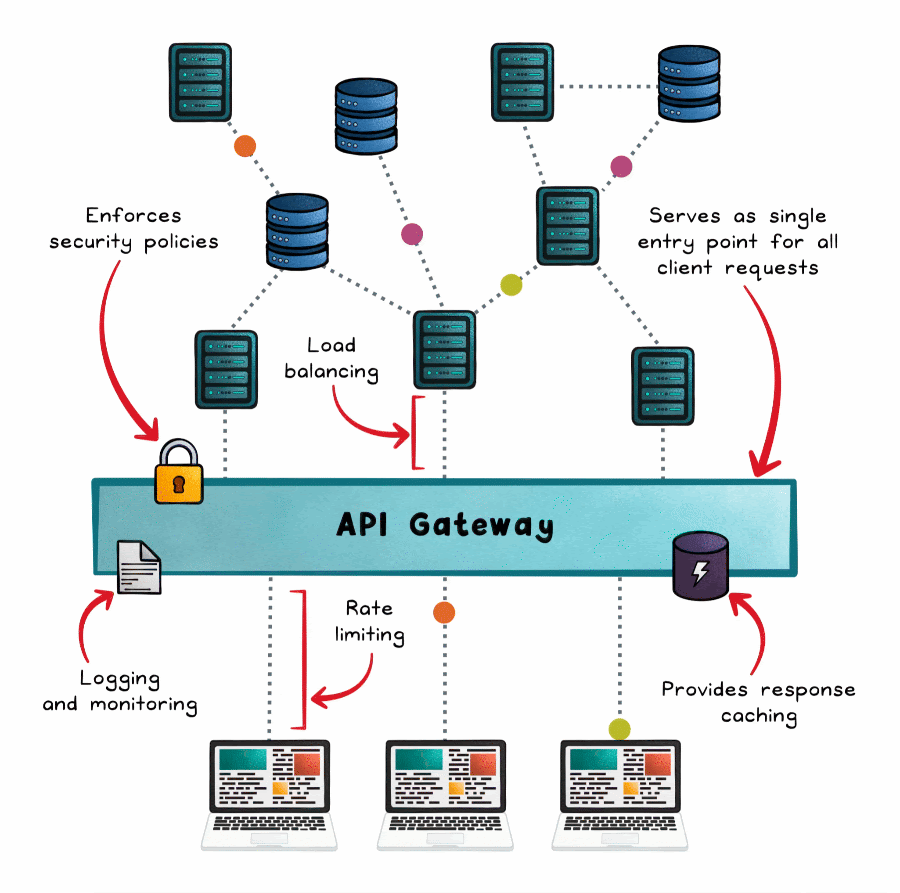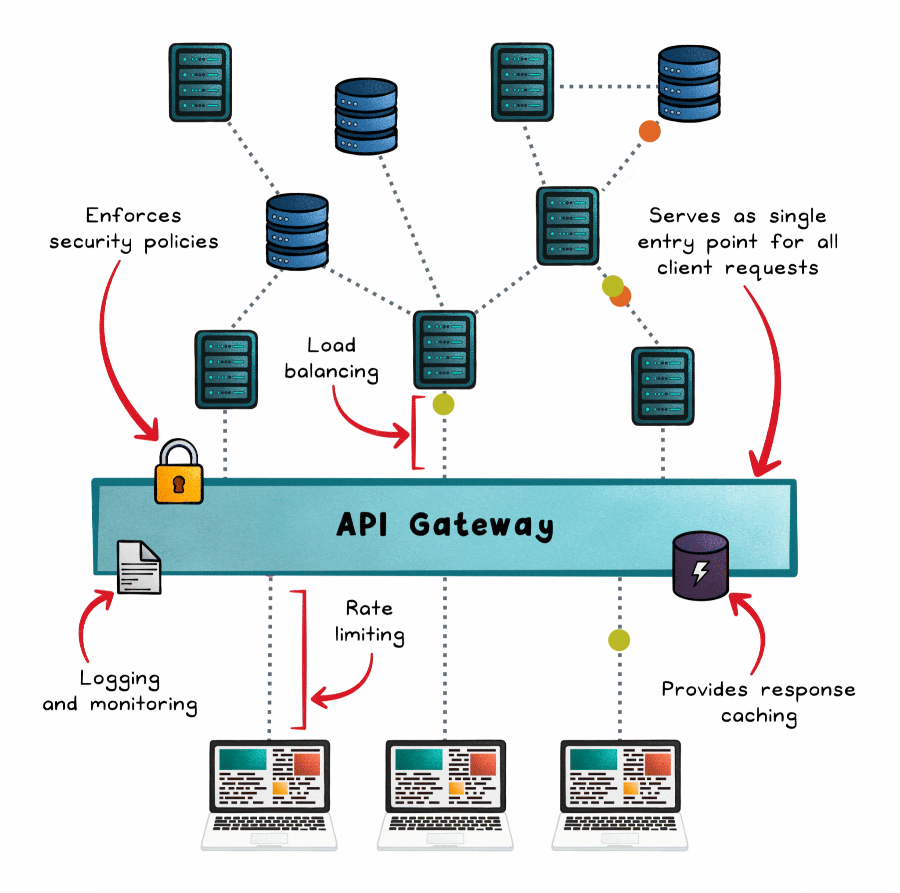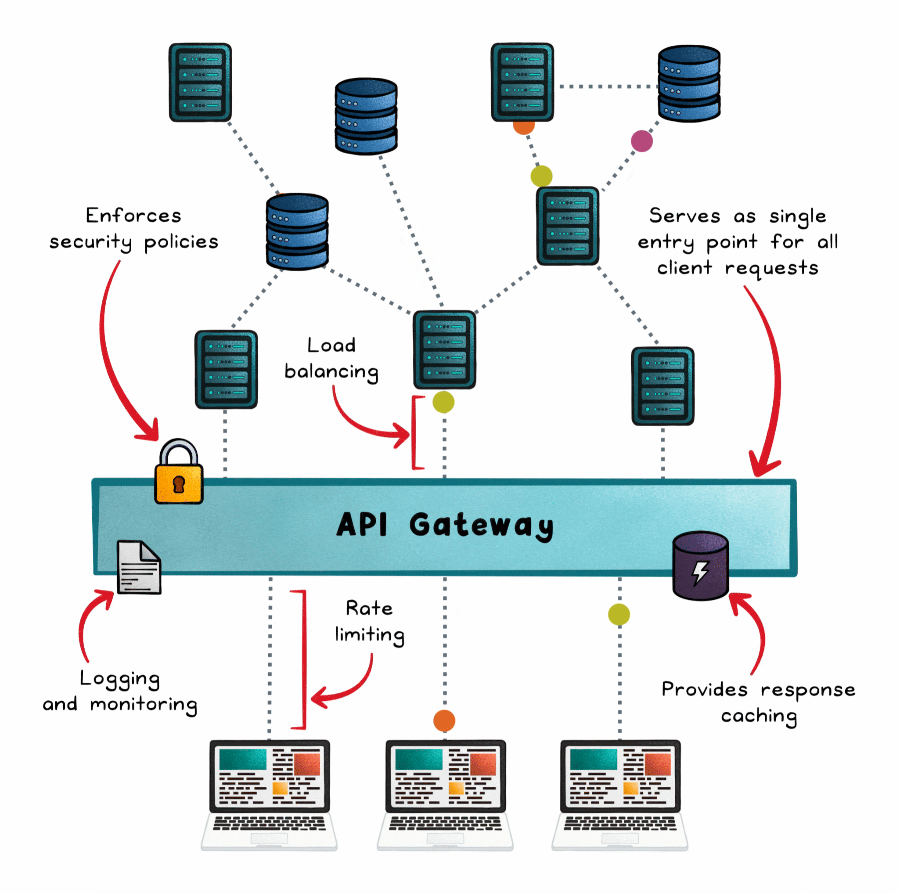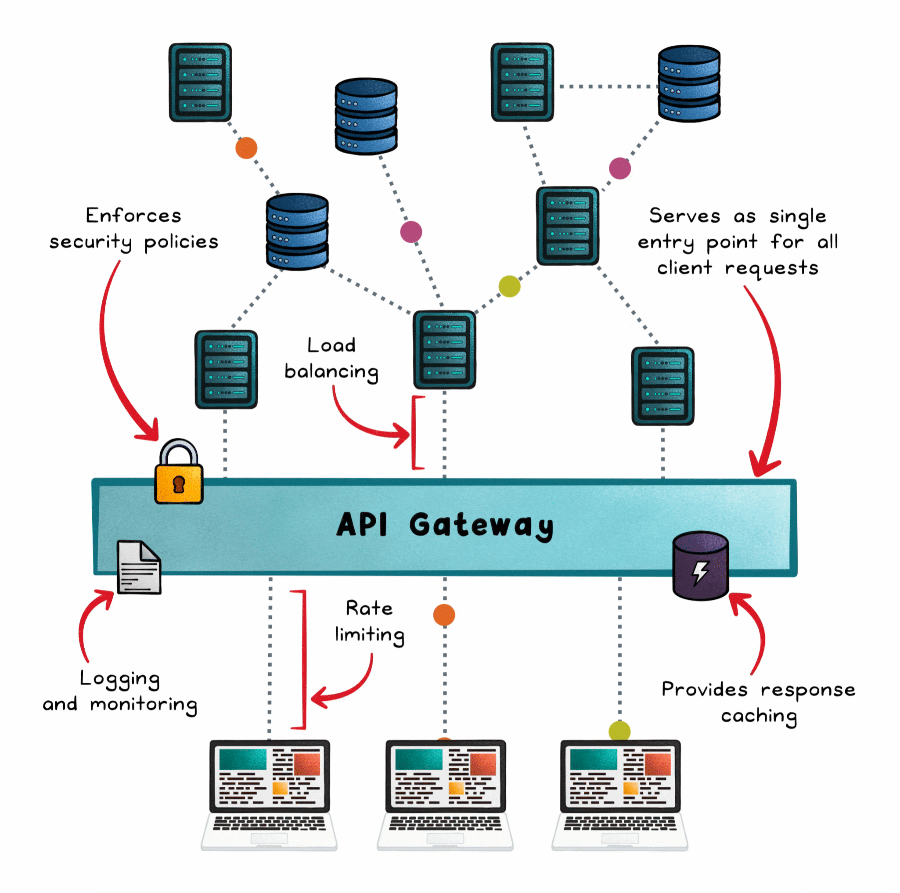
An API gateway is a single entry point for API traffic. It doesn’t just route, it manages, secures, and shapes requests before they hit your backend.
A typical request flow through an API gateway:
Initial handling — All API requests hit the gateway, not individual services.
Validation — Ensures the request format is correct.
Security checks — Filters against allow/deny lists.
Authentication & authorization — Verifies credentials, tokens, and permissions.
Rate limiting — Enforces per-client quotas.
Service discovery & routing — Determines which backend service should handle the request.
Protocol translation — Bridges formats (HTTP ↔ gRPC/WebSocket, etc).
Response aggregation — Combines results from multiple services if needed.
Response delivery — Returns the composed result to the client.
Monitoring & caching — Logs metrics, applies caching, and triggers fault handling (circuit breaking).
Key strengths:
Centralized authentication and authorization
Traffic shaping (rate limits, quotas)
Request/response transformation
Observability and logging
Protocol bridging
When to Use Each
Simple high-availability setup? A load balancer might be all you need.
Public APIs, many services, or complex client interactions? You’ll benefit from an API gateway’s centralized policy management.
At scale, many production systems run both.
Load Balancer → API Gateway → Services.
With the LB ensuring availability and the gateway enforcing API rules.
Common Pitfalls
Gateway bloat — Heavy transformations and orchestration in the gateway increase latency. Keep business logic in services.
Edge-only auth — Always revalidate tokens downstream for defense in depth.
Sticky sessions at the LB — Often a smell; aim for stateless services or shared session storage.
Single point of failure — Deploy both gateways and load balancers across zones/regions.
Final Thoughts
A load balancer keeps your app available and fast.
An API gateway keeps it secure and well-governed.
They’re not competitors, they’re partners. In larger systems, one handles the traffic, the other enforces the rules. Together, they form a strong, reliable edge for your architecture.
Subscribe to get simple-to-understand, visual, and engaging system design articles straight to your inbox: