Get our Architecture Patterns Playbook for FREE on newsletter signup:
The Only Cloud-native Kafka Implementation Validated by Jepsen
Presented by Bufstream
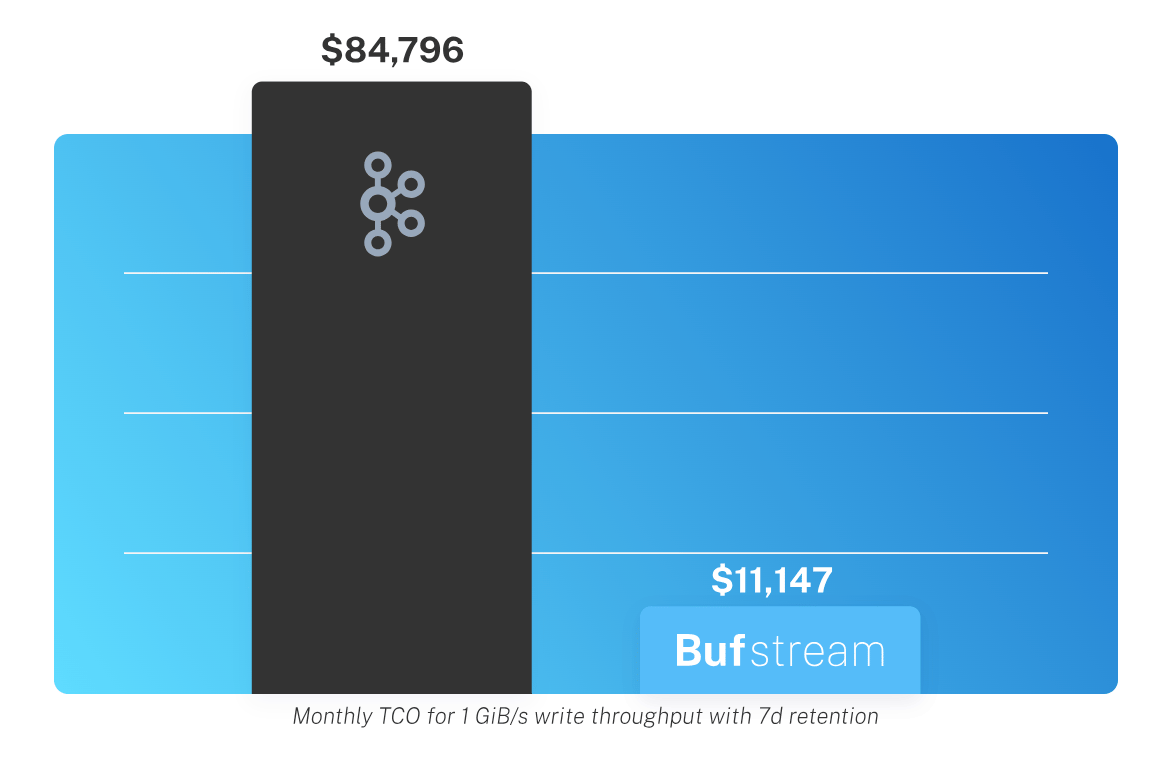
Bufstream is the only cloud-native Kafka implementation independently validated by Jepsen, passing the gold standard for distributed systems testing. It’s built for the modern enterprise—stateless, auto-scaling, schema-aware, and 8x cheaper than self-managed Kafka.
Designed for high-throughput workloads, Bufstream is ready for organizations that struggle with Kafka scalability, cloud cost control, and data quality.
Find out how Bufstream can improve your Kafka implementation in this article:
A Guide to Cloud Resource Optimization and Cost Management
An engineer is debugging and adds a bunch of logs. The engineer forgets to remove those logs. The team also never set a retention policy.
The end of the month comes, and with it comes the eye-watering cloud bill.
You’ve probably heard these kinds of cloud bill horror stories and maybe even witnessed them firsthand—hopefully you weren’t this engineer.
These stories illustrate the importance of effective cloud resource management from a cost perspective. The other side is performance.
Cloud resource management is an intricate balance between the cloud's expansive capabilities and the need to keep costs streamlined.
To be scalable, performant, and cost-effective, operations must achieve this balance.
Today we’ll be looking into how we can achieve this balance.
Let's jump in!
Understanding Cloud Costs and Resource Utilization
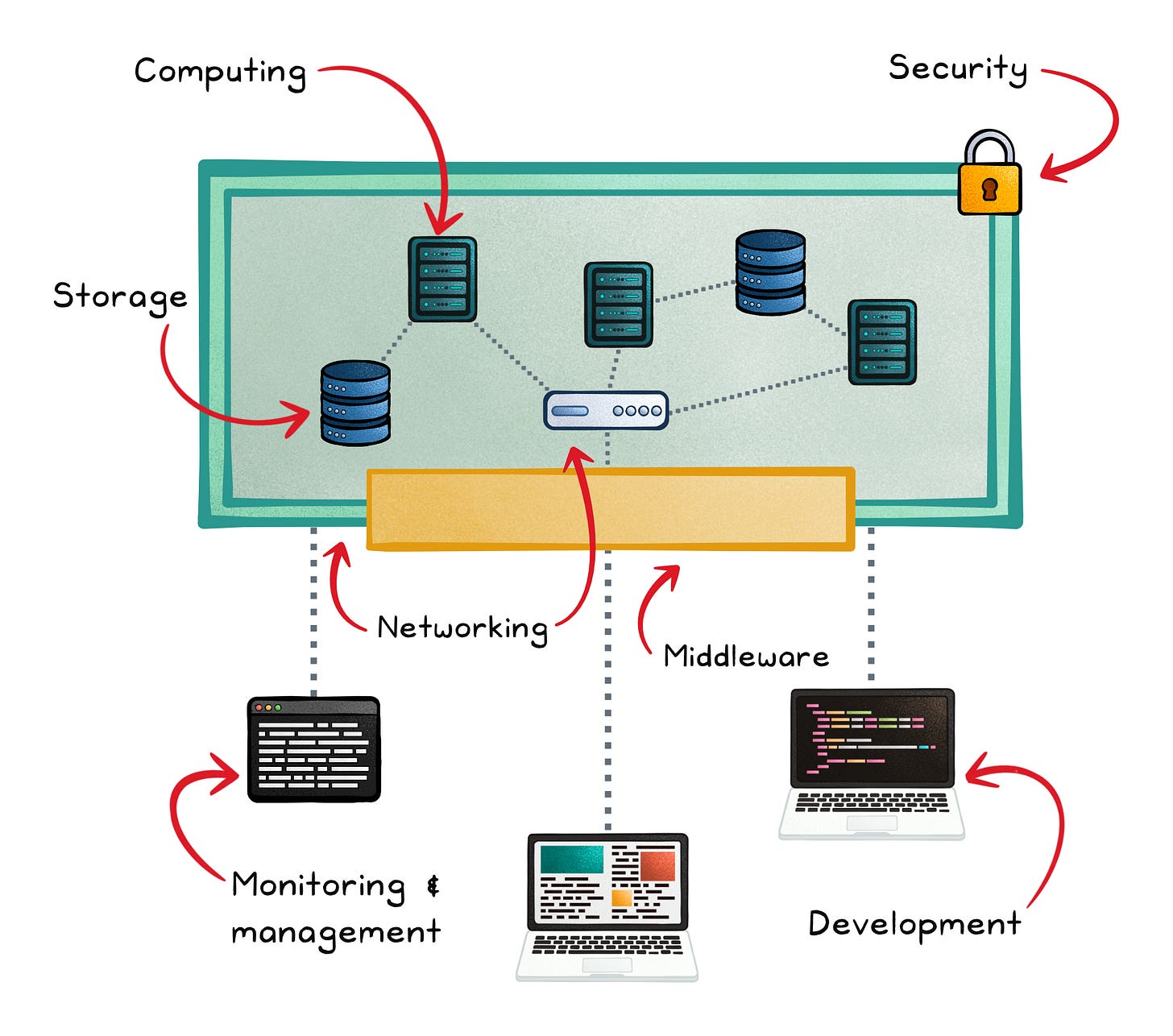
Cloud computing is built around key resources like compute instances, storage solutions, and networking services.
Without servers, our applications cannot run. Without networking services, various components won’t be connected. And without storage, our applications would technically still run—albeit severely limited.
Each has a unique pricing model, affecting the overall cost of cloud operations.
The performance and cost implications of compute instances are significant, directly influencing operational efficiency and financial outlay.
Storage costs fluctuate with capacity needs and the speed of access, requiring strategic decisions based on data volume and retrieval rates.
Networking costs are affected by the volume of data transfer and the bandwidth requirements, making efficient data management and network usage critical for cost-effective cloud deployment
Mismanaged resources inflate expenses. Yet, over-provisioning does not necessarily result in better performance.
Understanding the correlation between resource management practices and their cost implications is the first step toward successful cloud resource optimization and cost management.
Strategies for Cloud Resource Optimization and Cost Management
An efficient cloud management approach strikes a balance between performance and cost-effectiveness.
The following are some key strategies to help strike that balance:
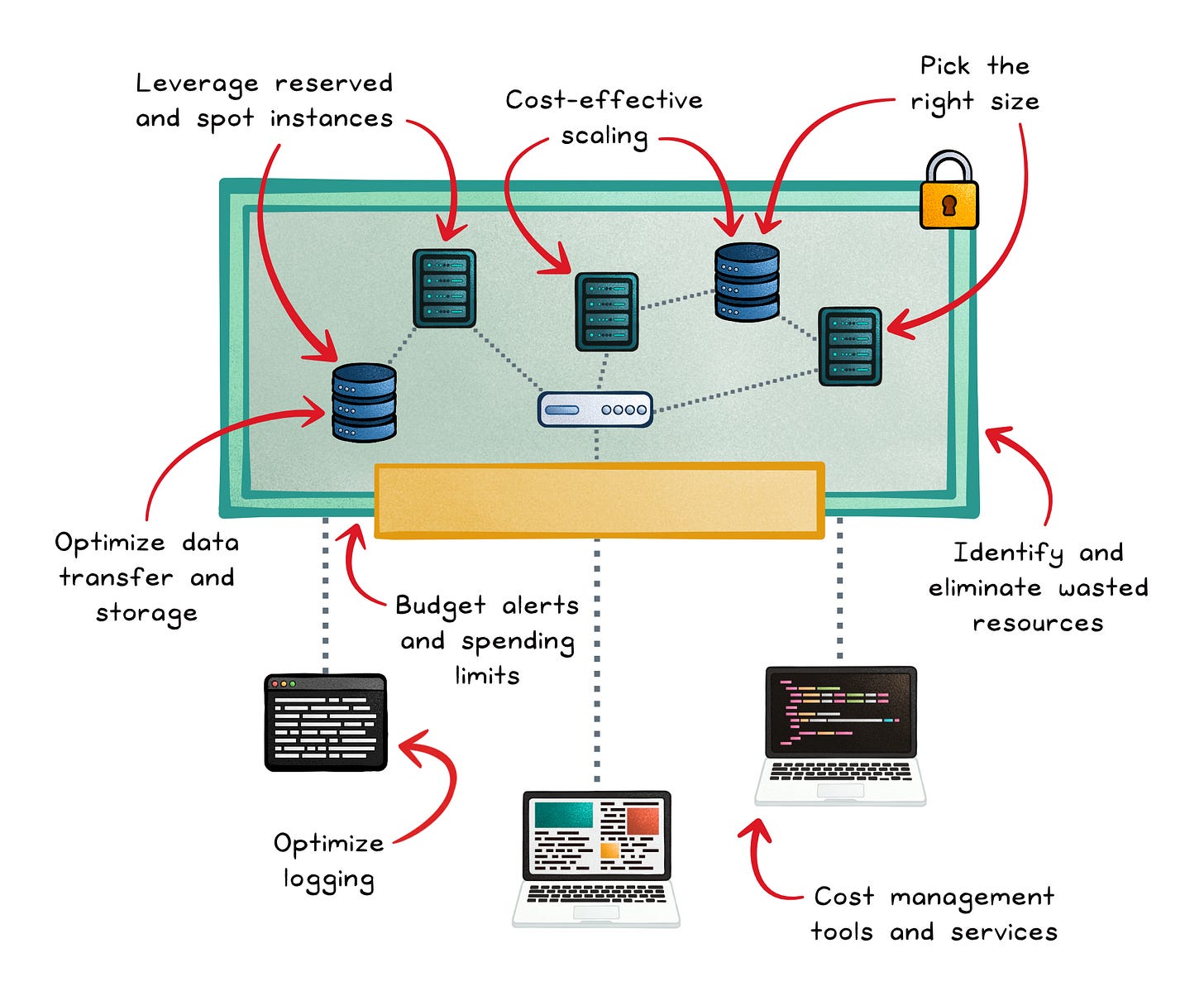
Right-sizing for efficiency and cost savings
By matching the allocation of cloud resources to actual requirements, right-sizing helps minimize waste and reduce expenses without compromising performance.
Finding the right configuration for this strategy requires a thorough analysis of workload requirements and resource usage patterns.
Cost-effective scaling with auto-scaling
Auto-scaling adapts to real-time demands.
It reduces resources during low-demand times and increases them during peak periods to avoid over-provisioning.
Leveraging reserved and spot instances
Reserved instances reduce costs for steady workloads, whereas spot instances provide a more cost-effective, flexible option for tasks that can wait.
Both strategies have lower costs when compared to on-demand prices.
Cost management tools and services
These tools come out of the box with each provider to assist with cloud spending management and optimization.
They can monitor spending habits, identify potential savings, and automate cost controls. Utilize them.
Budget alerts and spending limits
We’ve all heard the horror stories, and you might have witnessed some firsthand of a service such as logs racking up eye-watering bills.
Setting alerts and limits helps prevent you from falling prey to these unexpected cost overruns.
These alerts notify you as you approach or exceed your budget limit, allowing you to take prompt action.
Optimizing logging to control cloud costs
Logs are essential but they can be costly if not managed correctly.
Optimize log practices by adjusting levels and retention policies. Reviews also help in keeping costs and insights in check.
Identifying and eliminating wasted resources
Frequent audits of cloud resources can identify instances, storage volumes, or services that are underutilized or unused and contribute to unnecessary costs.
This information can then be used to repurpose or remove those resources.
Cost management tools like AWS Cost Explorer should be picking up on these for you, so start there.
Optimizing data transfer and storage costs
Strategies like selecting the appropriate storage class, managing data transfer wisely, and leveraging content delivery networks can significantly reduce the costs of data storage and movement.
Best Practices in Cloud Cost Management and Resource Optimization
Effective cloud management relies on a few key practices that ensure cost efficiency and optimal resource utilization.
One of them is tagging, a method that involves assigning labels to cloud resources to track usage and spending accurately.
This fundamental method gives organizations the ability to categorize spending on a granular level, providing visibility into their cloud environment and allowing for better decision-making and financial accountability.
Adopting policy-driven optimization is another strategy.
Besides streamlining operations, it ensures that resources are aligned with actual needs, preventing waste and reducing expenses.
And as mentioned previously, cloud cost management tools provide detailed insights into cloud spending, allowing organizations to automate optimizations and identify cost-saving opportunities.
This is not an exhaustive list but it highlights the importance of strategic planning and continuous monitoring in achieving an efficient and cost-effective cloud environment.
Challenges in Balancing Performance and Cost
Balancing performance with cost in cloud environments is a difficult challenge; from predicting workload patterns to managing costs across multiple cloud services.
The complexity of optimizing resources without compromising performance necessitates sophisticated strategies, especially in multi-cloud scenarios where each platform has its pricing model and optimization tools.
Depending on the size of the organization you’re working with, different approaches will be advisable. In saying that, the approach will very likely be centered around the strategies I mentioned above.
Wrapping up
Our applications run in the cloud, and generally, a significant portion of an organization’s expenses are from the cloud. Integrating cost management with cloud resource optimization isn't just beneficial—it's essential.
Actual implementation of resource optimization and cost management can be quite difficult. Thankfully, the best practices for cloud resource management are quite clear and serve as a guiding hand.
Subscribe to get simple-to-understand, visual, and engaging system design articles straight to your inbox: